Go based implementation of an MCP server for Azure Cosmos DB
This is a Go based implementation of an MCP server for Azure Cosmos DB using the Azure SDK for Go and the official MCP Go SDK.
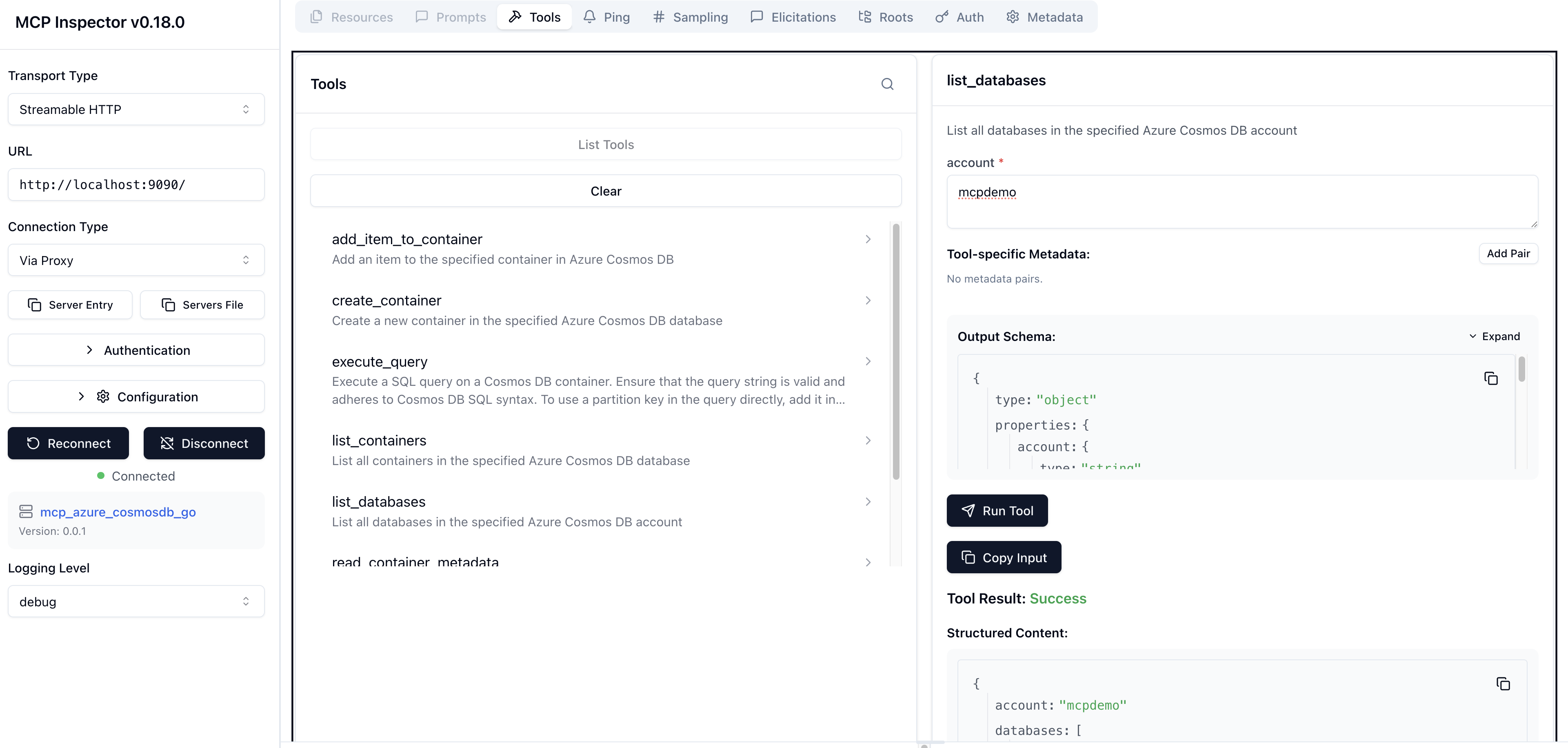
It exposes the following tools for interacting with Azure Cosmos DB:
- List Databases: Retrieve a list of all databases in a Cosmos DB account.
- List Containers: Retrieve a list of all containers in a specific database.
- Read Container Metadata: Fetch metadata or configuration details of a specific container.
- Create Container: Create a new container in a specified database with a defined partition key.
- Add Item to Container: Add a new item to a specified container in a database.
- Read Item: Read a specific item from a container using its ID and partition key.
- Execute Query: Execute a SQL query on a Cosmos DB container with optional partition key scoping.
⚠️ This project is not intended to replace the Azure MCP Server or Azure Cosmos DB MCP Toolkit. Rather, it serves as an experimental learning tool that demonstrates how to combine the Azure Go SDK and MCP Go SDK to build AI tooling for Azure Cosmos DB.
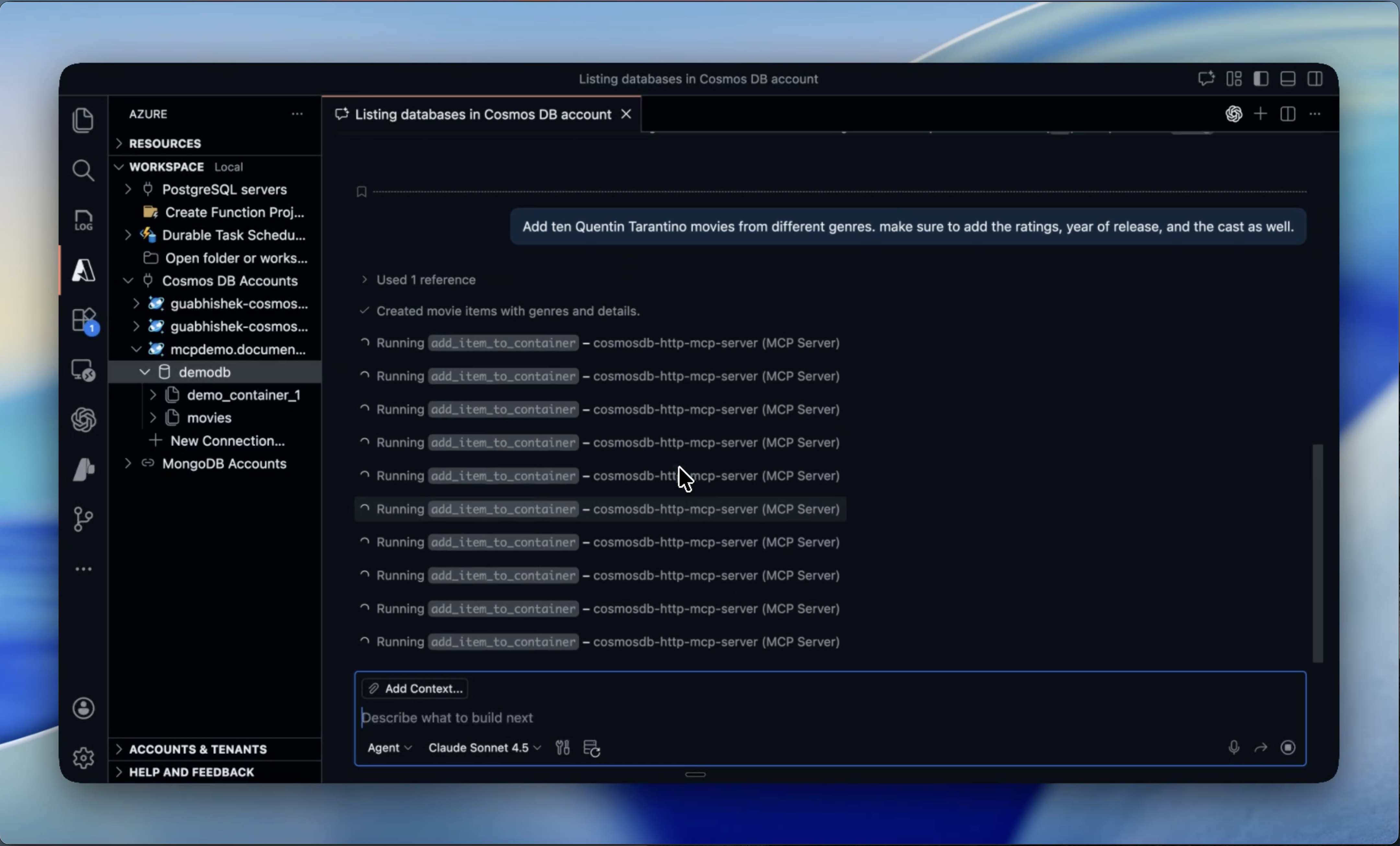
▶️ Here is a demo using Agent Mode in Visual Studio Code:
🚀 How to Run
To start with, clone the GitHub repo and build the binary:
git clone https://github.com/abhirockzz/mcp_cosmosdb_go
cd mcp_cosmosdb_go
go build -o mcp_azure_cosmosdb_go main.go
Note: The MCP server uses the DefaultAzureCredential implementation from the Azure SDK for Go to authenticate with Azure Cosmos DB. This means that you can authenticate using various methods, including environment variables, managed identity, or Azure CLI login, among others.
This MCP server supports both Streamable HTTP and Stdio transports. You can run the MCP server in two modes:
- Locally on your machine as an HTTP server, or
stdioprocess - Deployed to a remote endpoint (like Azure App Service, Azure Container Apps, etc.) as an HTTP(s) server
💻 Local mode
Thanks to Streamable HTTP support, you can easily run this MCP server as an HTTP server locally on your machine.
Login using Azure CLI (az login), or the Azure Developer CLI (azd auth login). Since the MCP server uses DefaultAzureCredential, it will authenticate as the identity logged in to the Azure CLI or the Azure Developer CLI.
The user principal (identity) you are logged in with should have permissions (control and data plane) to execute CRUD operations on database, container, and items.
🌐 HTTP server
Start the server:
export COSMOSDB_MCP_SERVER_MODE=http
./mcp_azure_cosmosdb_go
This will start the server on port 9090 by default. You can change the port by setting the PORT environment variable.
How you configure the MCP server will differ based on the MCP client/tool you use. For VS Code you can follow these instructions on how to configure this server using a mcp.json file.
Here is an example of the mcp.json configuration for the HTTP server:
{
"servers": {
"mcp_azure_cosmosdb_go_http": {
"type": "http",
"url": "http://localhost:9090"
}
}
//other MCP servers...
}
Change the port if you have configured a different one.
🖥️ Stdio server
Here is an example of the mcp.json configuration for the stdio mode:
{
"servers": {
"mcp_azure_cosmosdb_go_stdio": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "./mcp_azure_cosmosdb_go"
}
}
//other MCP servers...
}
Once you have configured the MCP server in your tool, you can start using it to interact with Azure Cosmos DB (just like in the demo shown above). For other tools like Claude Code, Claude Desktop, etc., refer to their respective documentation on how to configure an MCP HTTP/stdio server.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are non-deterministic by nature and can make mistakes. Always validate the results and queries before making any decisions based on them.
☁️ Remote endpoint
You can also deploy this MCP server to any cloud service (like Azure App Service, Azure Container Apps, etc.) and expose it as an HTTP(s) endpoint. The Azure service should support Managed Identity, and the MCP server will automatically pick up the credentials using the DefaultAzureCredential implementation.
⛔️ This execution mode is not recommended. Use this only for testing purposes. This is because, although MCP server can access Azure Cosmos DB securely using Managed Identity, it does not authenticate (or authorize) clients yet - anyone who can access the endpoint can execute operations on your Cosmos DB account.
🧪 Local dev and testing
Use MCP inspector - make mcp_inspector